In times of uncertainty, one of the best things we can do to ease our fears is to educate ourselves with research, facts, and data. Digging into past experiences by reviewing historical trends and understanding the peaks and valleys of what’s come before us is one of the many ways we can confidently evaluate any situation. With concerns of a global recession on everyone’s minds today, it’s important to take an objective look at what has transpired over the years and how the housing market has successfully weathered these storms.
1. The Market Today Is Vastly Different from 2008
We all remember 2008.
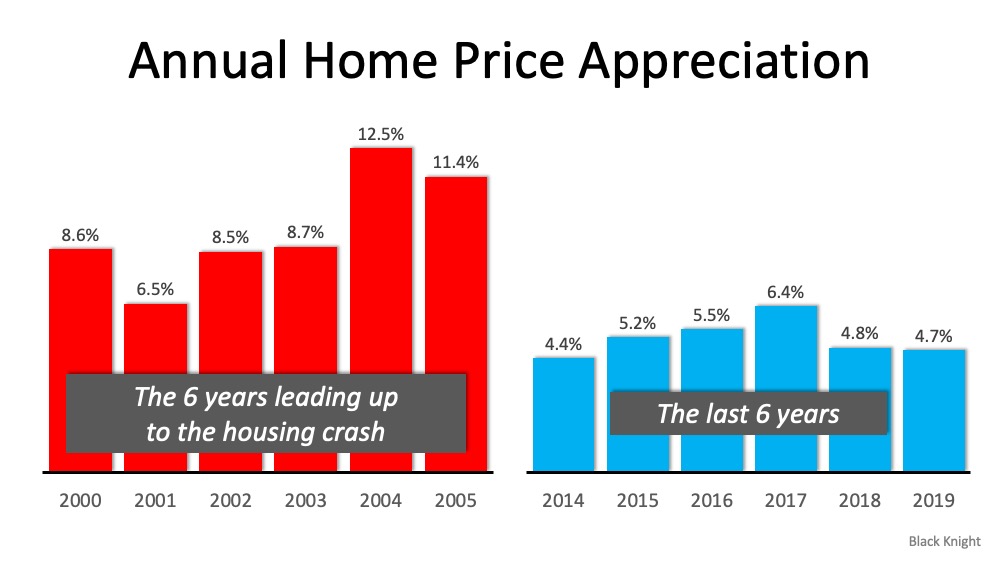
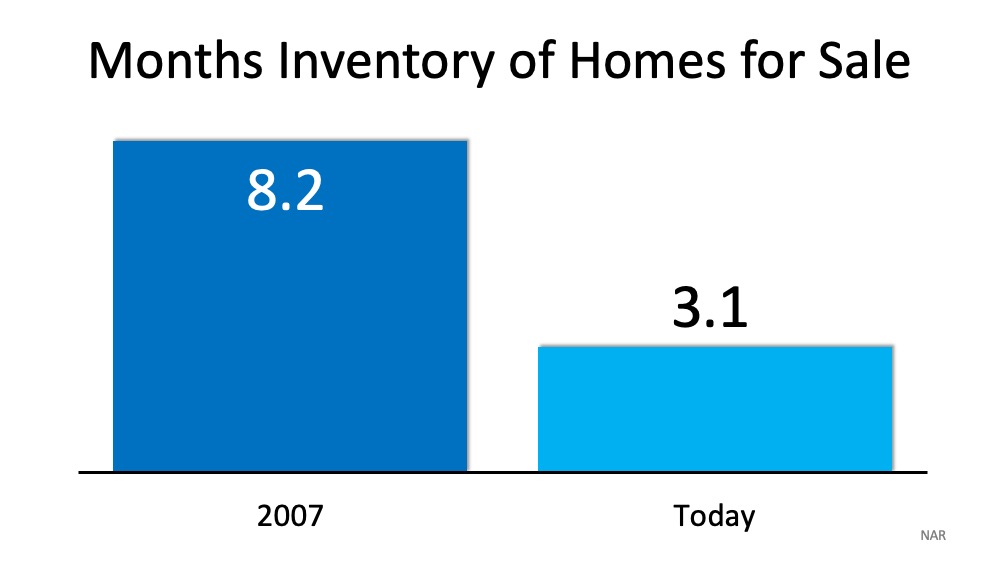
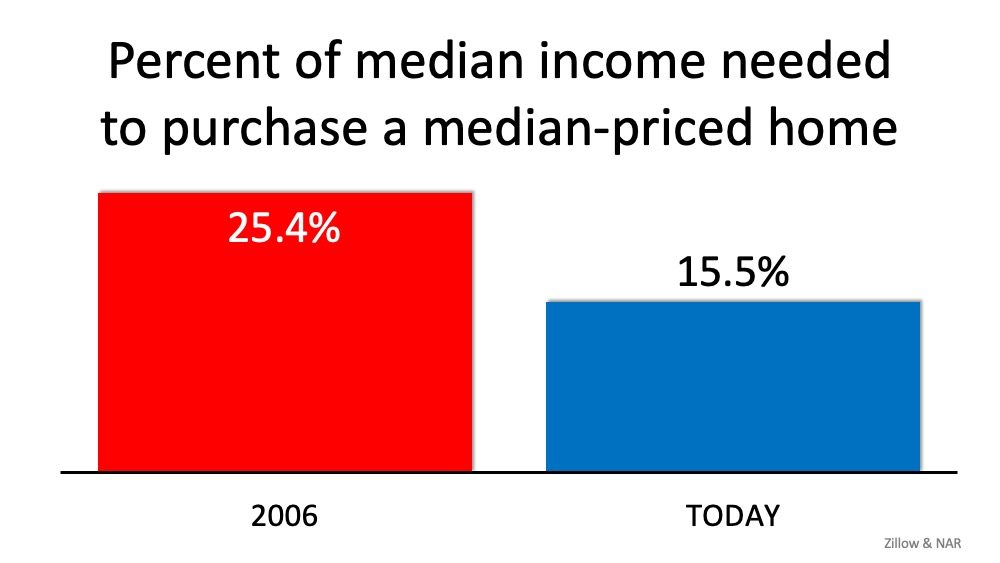
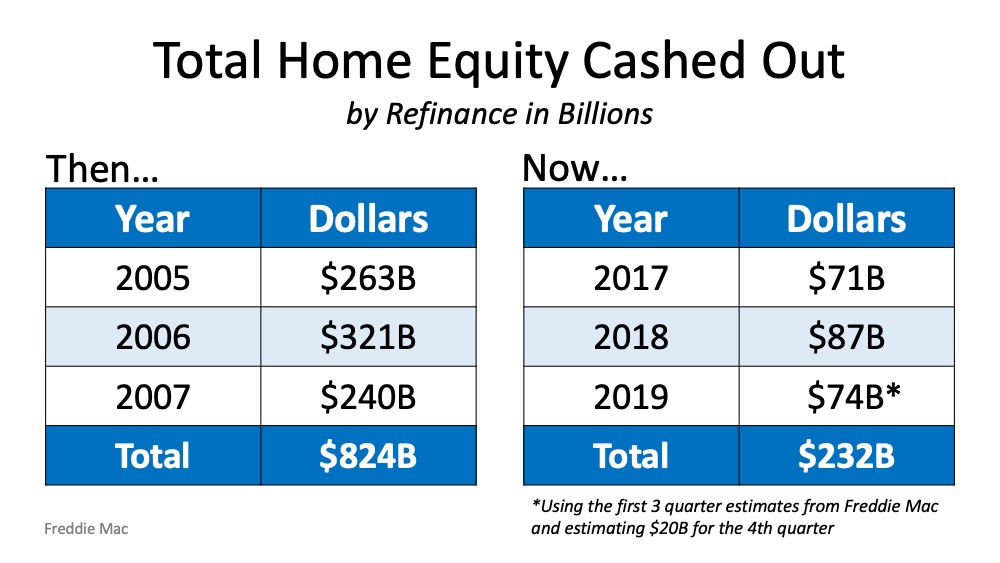
This is not 2008. Today’s market conditions are far from the time when housing was a key factor that triggered a recession. From easy-to-access mortgages to skyrocketing home price appreciation, a surplus of inventory, excessive equity-tapping, and more – we’re not where we were 12 years ago. None of those factors are in play today. Rest assured,
housing is not a catalyst that could spiral us back to that time or place.
According to Danielle Hale, Chief Economist at Realtor.com, if there is a recession:
"It will be different than the Great Recession. Things unraveled pretty quickly, and then the recovery was pretty slow. I would expect this to be milder. There's no dysfunction in the banking system, we don't have many households who are overleveraged with their mortgage payments and are potentially in trouble."
In addition, the
Goldman Sachs GDP Forecast released this week indicates that although there is no growth anticipated immediately, gains are forecasted heading into the second half of this year and getting even stronger in early 2021.
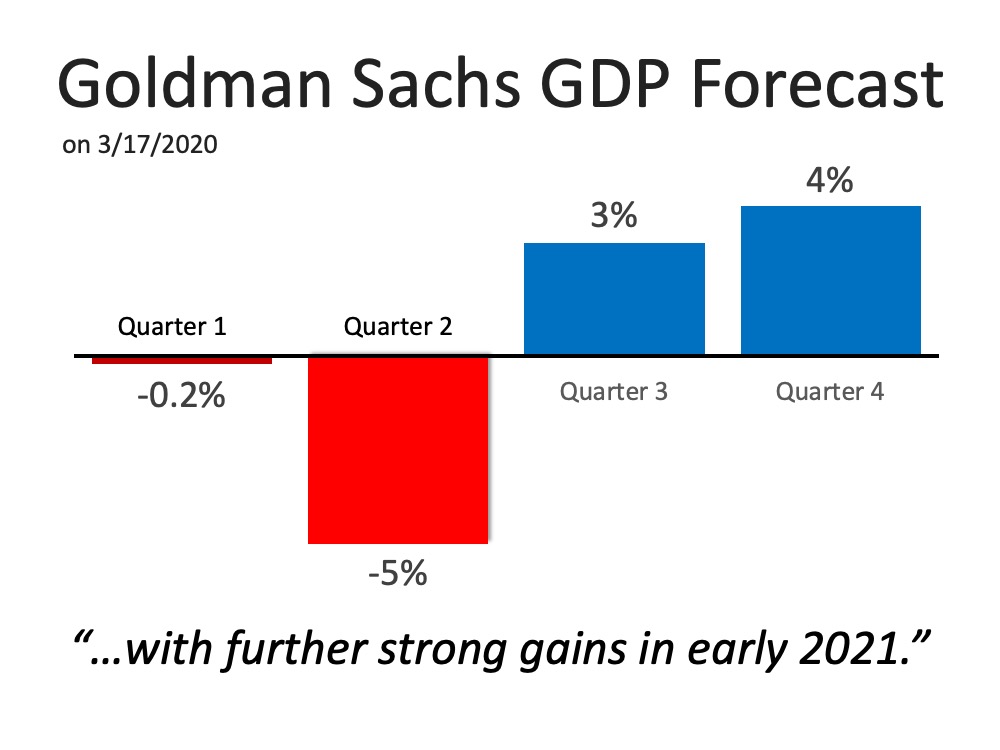
Both of these expert sources indicate this is a momentary event in time, not a collapse of the financial industry. It is a drop that will rebound quickly, a stark difference to the crash of 2008 that failed to get back to a sense of normal for almost four years. Although it poses plenty of near-term financial challenges, a potential recession this year is not a repeat of the long-term housing market crash we remember all too well.
2. A Recession Does Not Equal a Housing Crisis
Next, take a look at the
past five recessions in U.S. history. Home values actually appreciated in three of them. It is true that they sank by almost 20% during the last recession, but as we’ve identified above, 2008 presented different circumstances. In the four previous recessions, home values depreciated only once (by less than 2%). In the other three, residential real estate values increased by 3.5%, 6.1%, and 6.6% (see below):
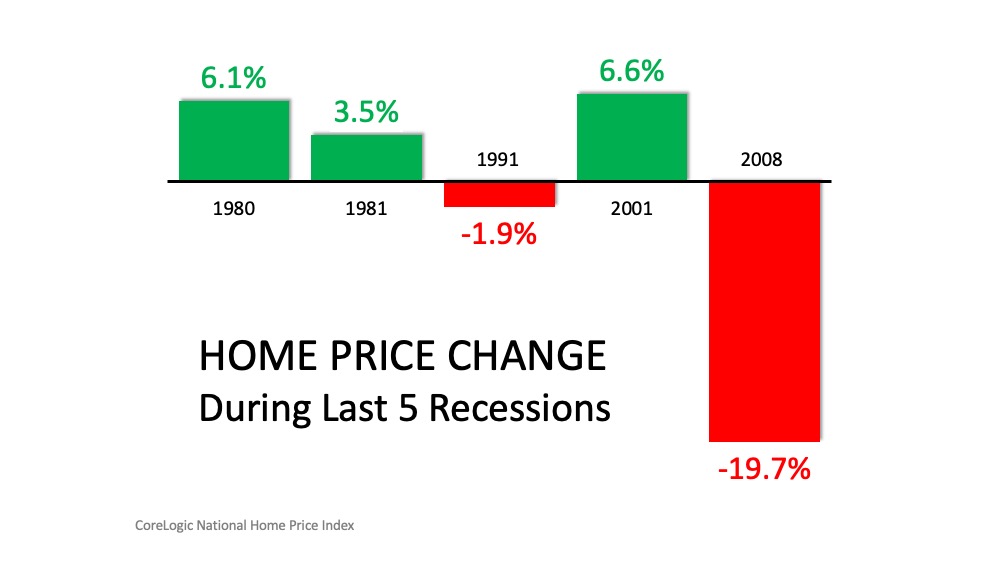
3. We Can Be Confident About What We Know
Concerns about the global impact COVID-19 will have on the economy are real. And they’re scary, as the health and wellness of our friends, families, and loved ones are high on everyone’s emotional radar.
“Several economists made clear that the extent of the economic wreckage will depend on factors such as how long the virus lasts, whether governments will loosen fiscal policy enough and can markets avoid freezing up.”
That said, we can be confident that, while we don’t know the exact impact the virus will have on the housing market, we do know that housing isn’t the driver.
The reasons we move – marriage, children, job changes, retirement, etc. – are steadfast parts of life. As noted in a recent piece in the
New York Times, “Everyone needs someplace to live.” That won’t change.
Bottom Line
Concerns about a recession are real, but housing isn’t the driver. If you have questions about what it means for your family’s homebuying or selling plans, let’s connect to discuss your needs.







![Buying a Home: Do You Know the Lingo? [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2020/03/09122748/20200313-MEM-EN-1046x1308.jpg)
